Publications
[1] The Impact of Investment Promotion on Multinational Production: Firm-level Evidence
with Jerónimo Carballo and Christian Volpe
Journal of Development Economics, vol. 180, March 2026
[Published Version] [Last WP Version] [Appendix]
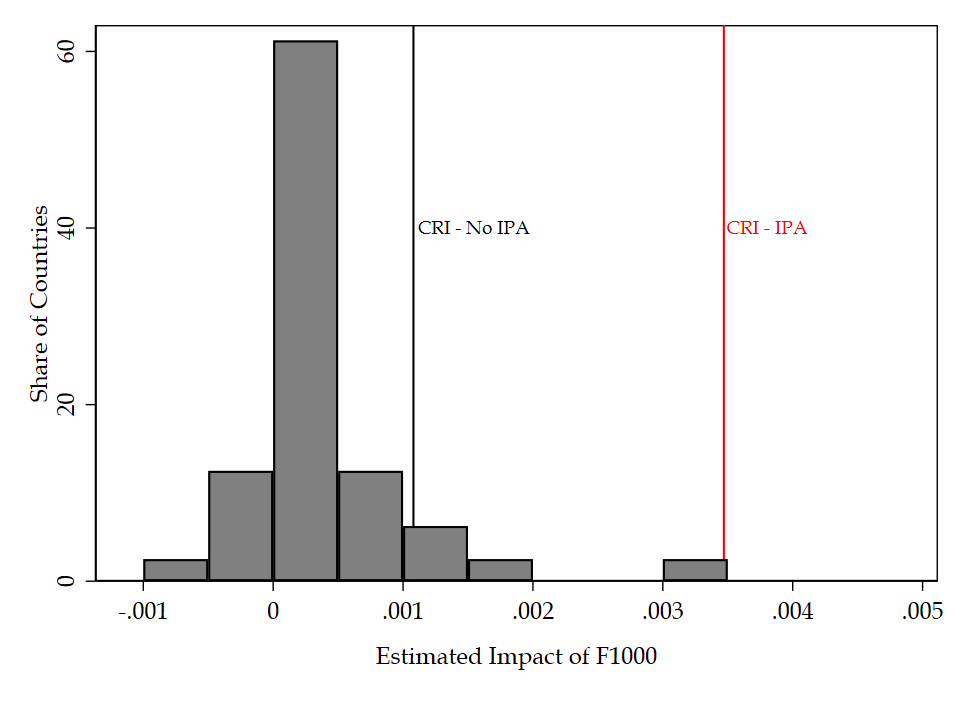
How do investment promotion agencies (IPAs) influence multinational companies’ decisions on where to establish foreign affiliates? This paper finds that while agency support significantly boosts a firm’s initial investment by resolving information asymmetries, it generally does not affect their subsequent expansion.
[2] Automatic Product Classification in International Trade: Machine Learning & Large Language Models
with Franco Riottini and Christian Volpe
Review of International Economics, vol. 34 (1), February 2026
[Published Version] [Last WP Version] [Appendix]
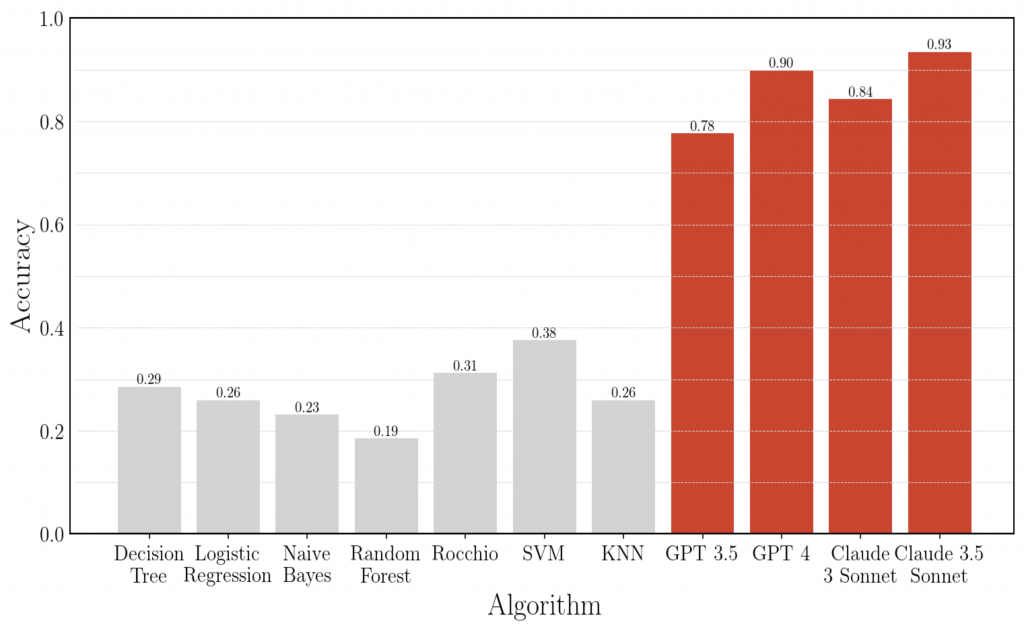
How can we accurately classify products based on text descriptions? This paper shows that while traditional machine learning models perform poorly outside their training data, large language models consistently achieve 70–90% accuracy, highlighting their value for unstructured data categorization.
Working Papers
[3] The Labor Market Effects of Multinational Entry [Last Version]
Best paper at 15th Conference on the Economics of Global Interactions (Wim Meeusen Prize)
Best student paper at Forum for Research in Empirical International Trade (FREIT – SETC 2025)
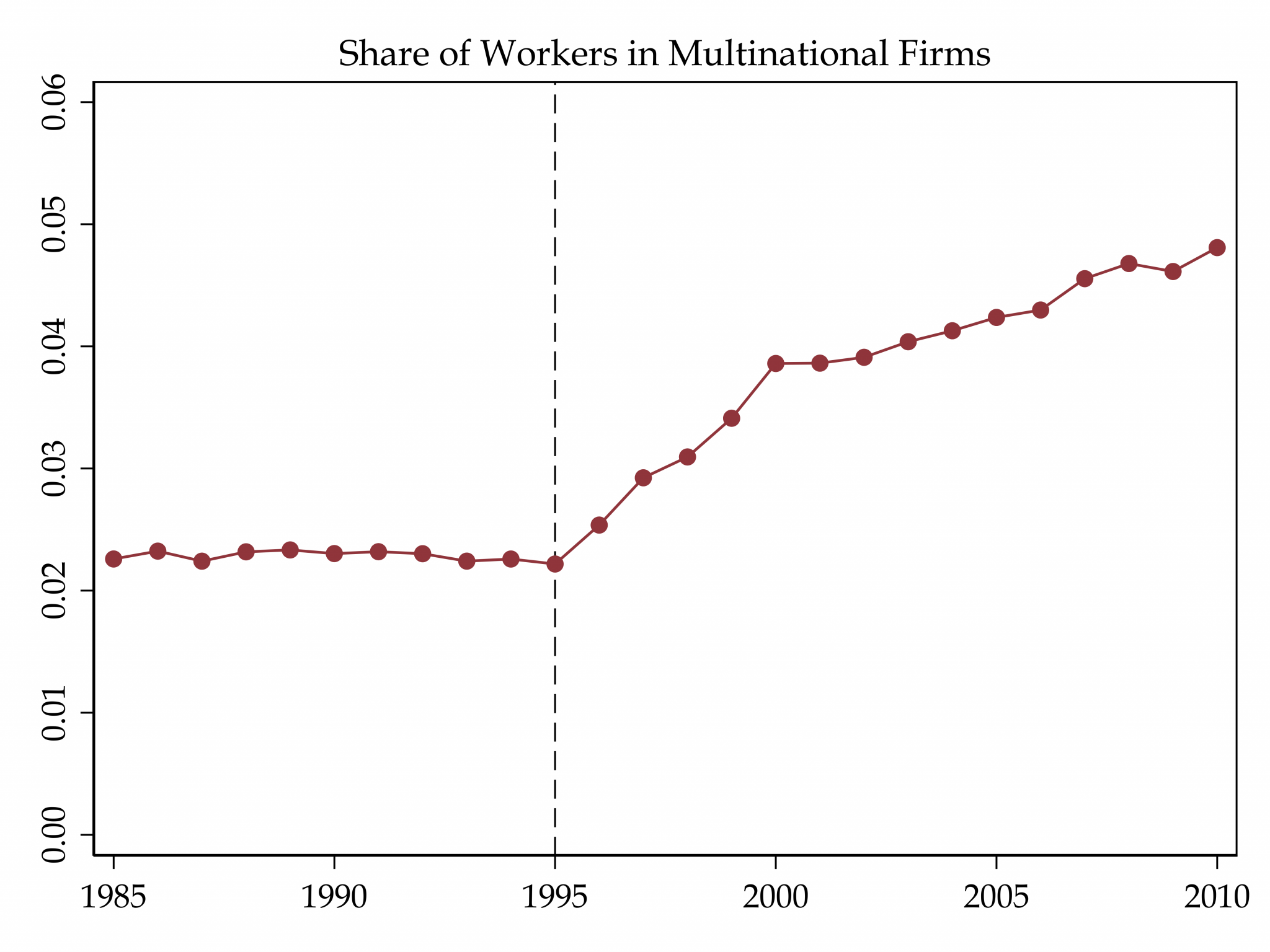
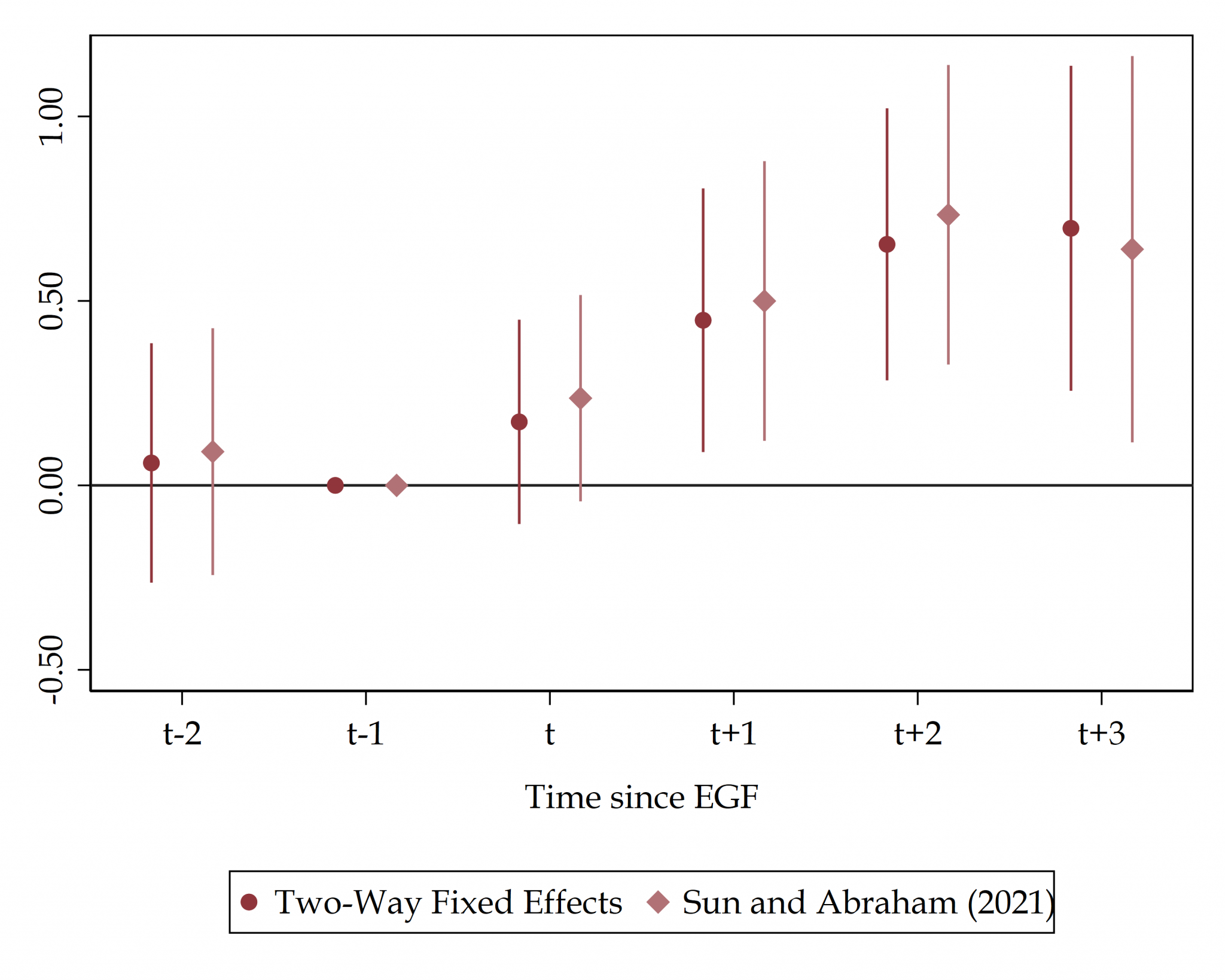
In 1995 a constitutional amendment opened Brazil to foreign investment, and within a decade 700,000 workers joined multinational firms. Using matched employer–employee data and a dynamic general equilibrium model, I show that multinational entry raised wages for college graduates but lowered pay and increased informality among less-educated workers; boosting growth while widening inequality.
Work in Progress
[4] Financial Constraints to Exporting: Experimental Evidence from Rwanda
with Jie Bai, Lauren Bergquist, and Christian Lippitsch
Funded by PEDL, IGC, and STEG – [AEA RCT Registry]
Fieldwork ongoing
Governments often enact policies to encourage firms to overcome financial barriers to exporting. In this randomized controlled trial, we evaluate the impact of a program that provides large subsidized loans to exporters. We generate exogenous variation in loan take-up through a randomized marketing campaign.
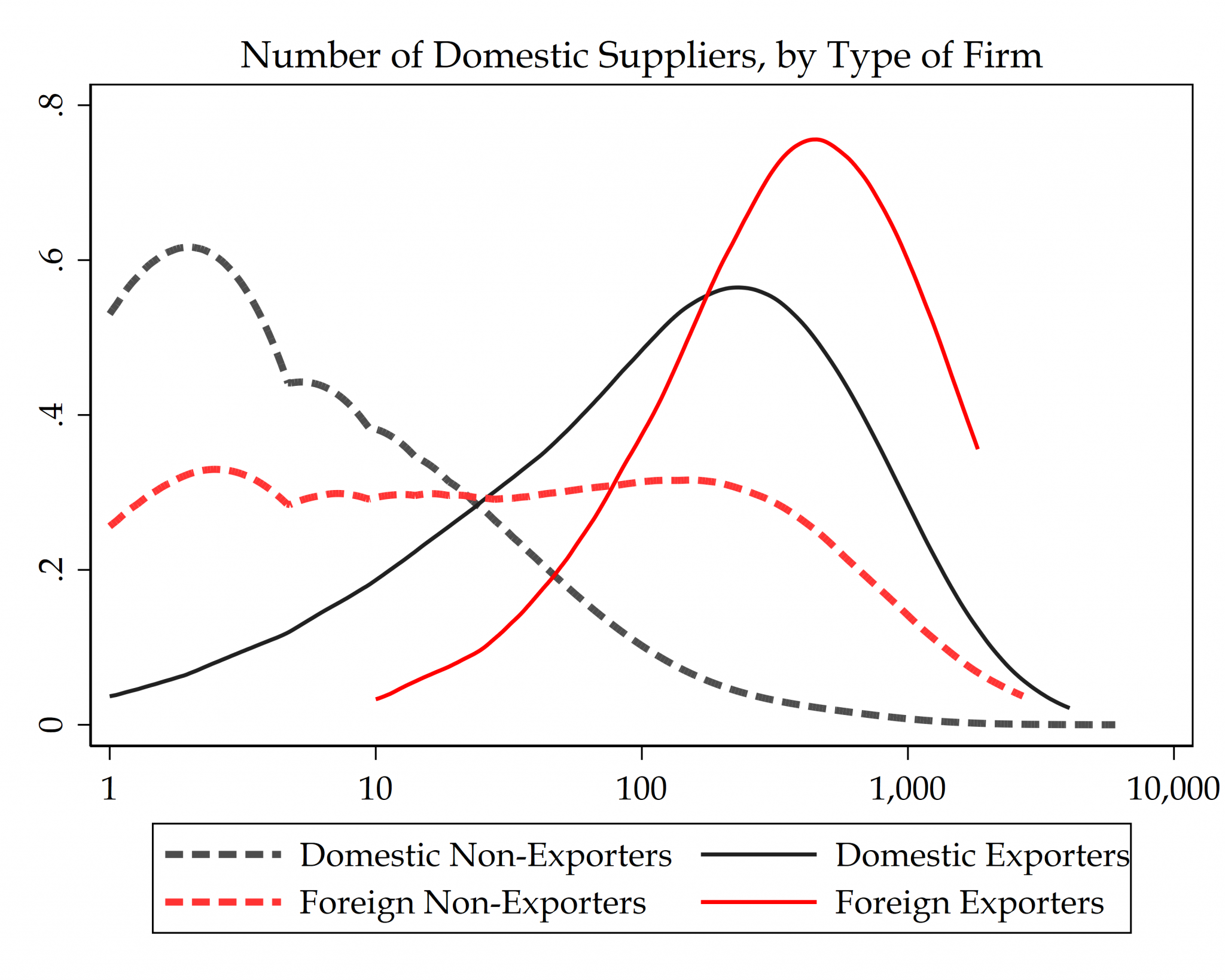
[5] Linkages with Multinationals: The Effect on Domestic Firms’ Exports
with Jerónimo Carballo, Gianmarco Ottaviano, and Christian Volpe
Draft available upon request
Do multinational enterprises affect the internationalization of their local suppliers? Using firm-to-firm data from Uruguay we find that supplying domestically to multinational companies significantly increases the probability of exporting for the first time.
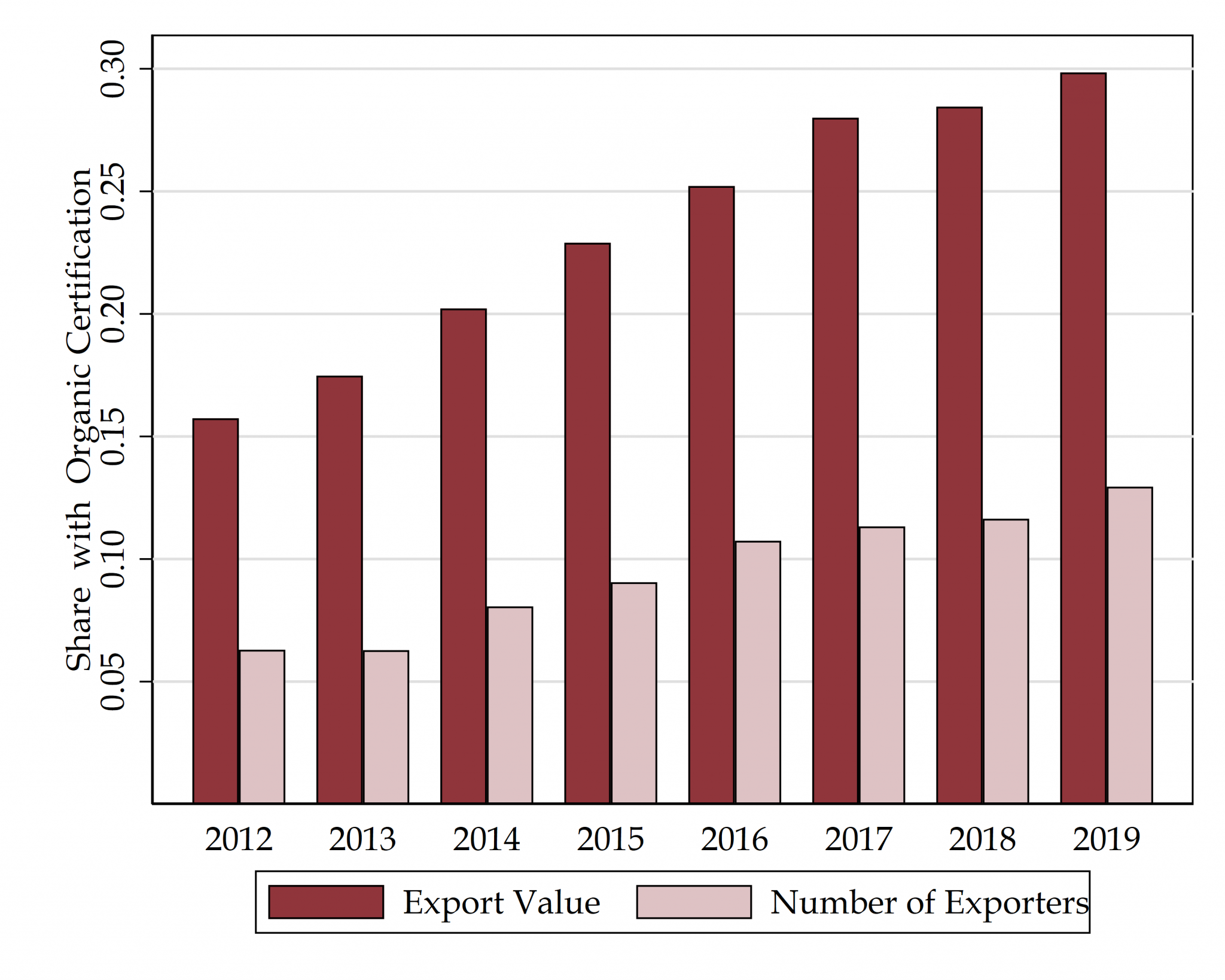
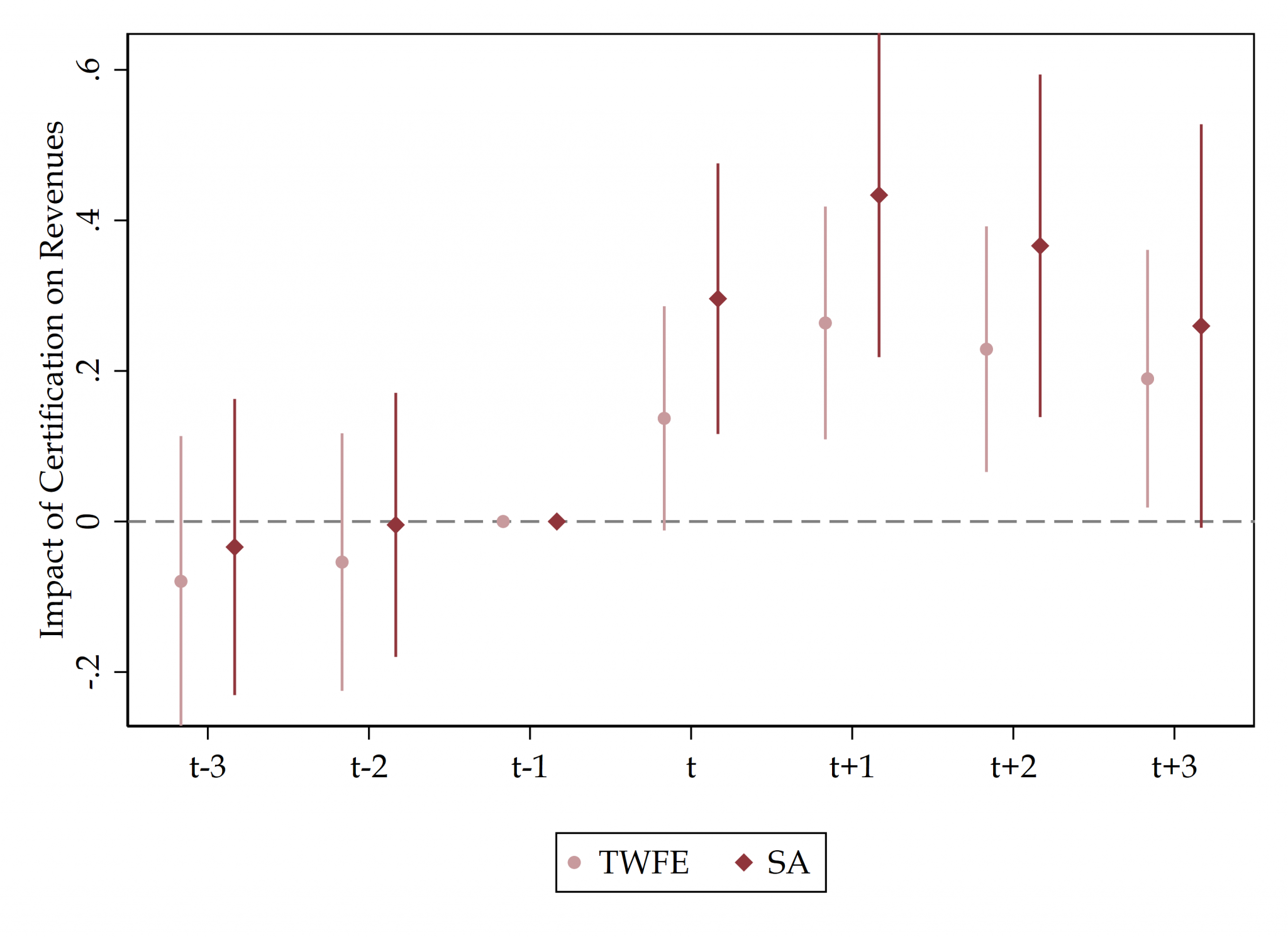
[6] The Value of Organic Certifications
with Franco Riottini, Gabriel Scattolo, Christian Volpe, and Lucas Zavala
Draft coming soon – [Preliminary Results at IDB Blog]
How does organic certification impact firms? Relying on both a structural model of voluntary certification along value chains and transaction-level customs data from several countries, we estimate the firm-level effects of organic certification.
[7] Striving for Quality: The Impact of Firm Certification in Rwanda
with Jie Bai, Vittorio Bassi, Lauren Bergquist, and Christian Lippitsch
Funded by IGC, Weiss Fund, Yale EGC, and STEG
Fieldwork ongoing
Firms in developing countries often struggle to upgrade and credibly signal the quality of their products. This project partners with the Rwandan Standards Board to test through an RCT how technical assistance for certification affects firms’ performance and supply chain dynamics.
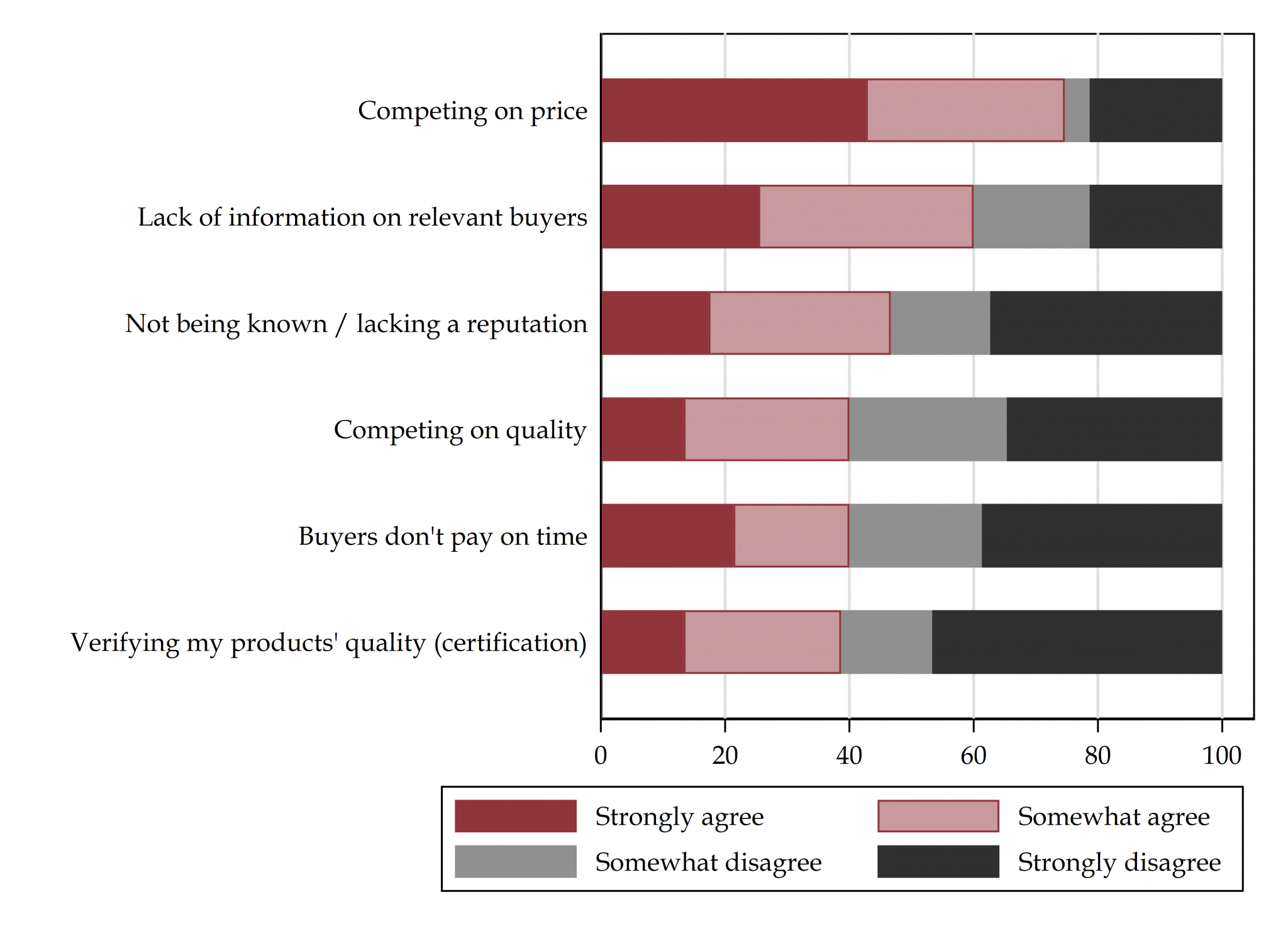
[8] Information Constraints in Domestic Supply Chains
with Jie Bai, Vittorio Bassi, Lauren Bergquist, and Christian Lippitsch
Funded by IGC – [Preliminary Survey at IGC Policy Brief]
Multinational firms in low-income countries frequently import inputs because they struggle to identify and verify reliable local suppliers. This project examines these information constraints in Rwanda and pilots, through a randomized controlled trial, a matching platform to connect large buyers with local suppliers.